Urban Health Platform
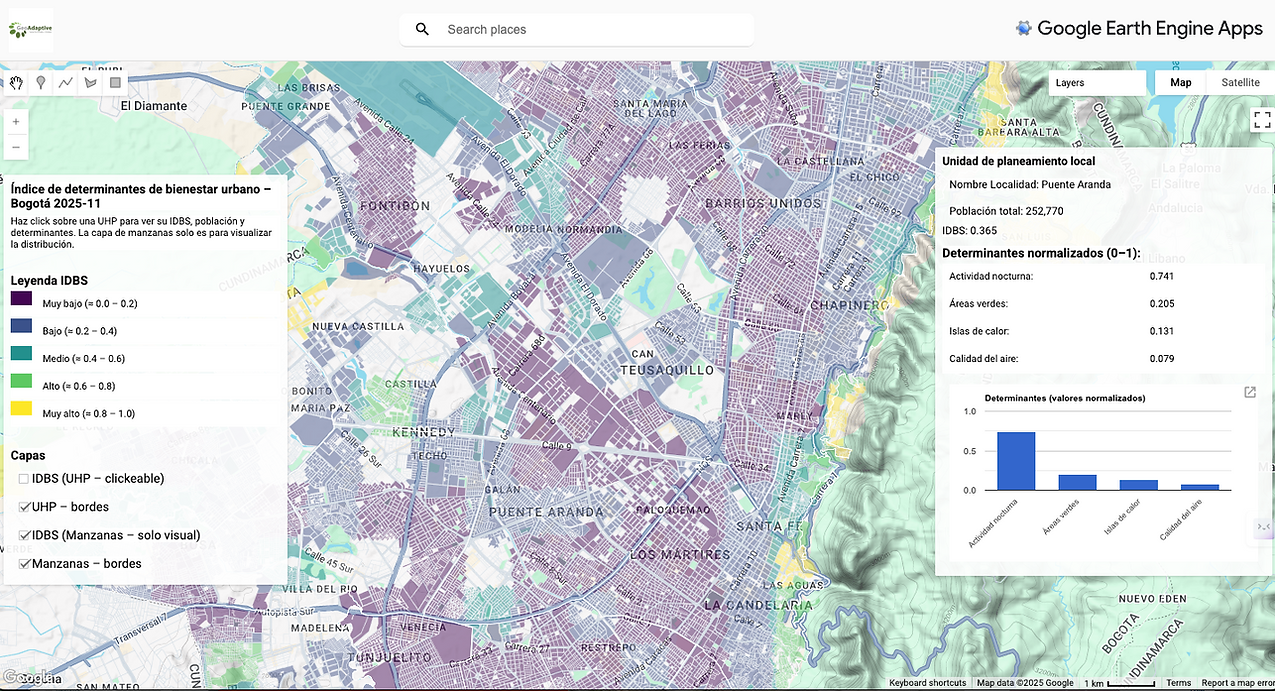
Index of Determinants of Well-being and Health (IDBS)
The Index of Determinants of Well-being and Health (IDBS) integrates environmental, social, climatic, ecological and economic variables to evaluate urban well-being at the neighborhood, commune or municipality level, allowing the identification of critical areas and guiding intervention policies.
The index has three main objectives:
-
To measure and compare urban well-being between areas within the same city.
-
Identify critical areas for climate adaptation, urban health, mobility, and ecology interventions.
-
Guide public investments and multilateral programs (e.g., Amazonia Forever, C40 Air Quality & Health, UN-Habitat UMF, PAHO Belém Health Action Plan) based on health co-benefits.
The IDBS consists of five dimensions, each constructed using standardized sub-indicators (0–1) and weighted according to scientific evidence, operational relevance, and international scalability.
Index dimensions:
-
Health
-
Climate Comfort
-
Social Services and Mobility
-
Ecological Environment
-
Economic Dynamics
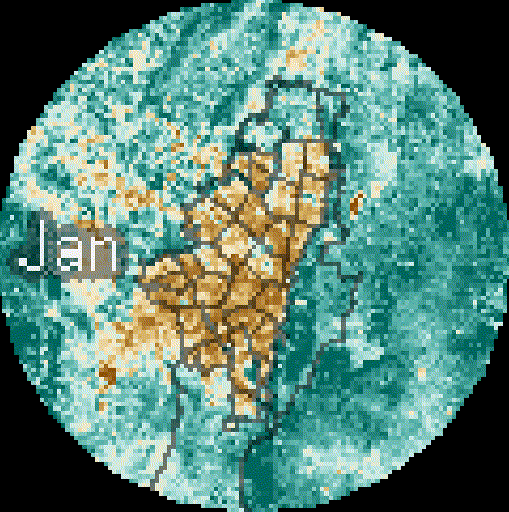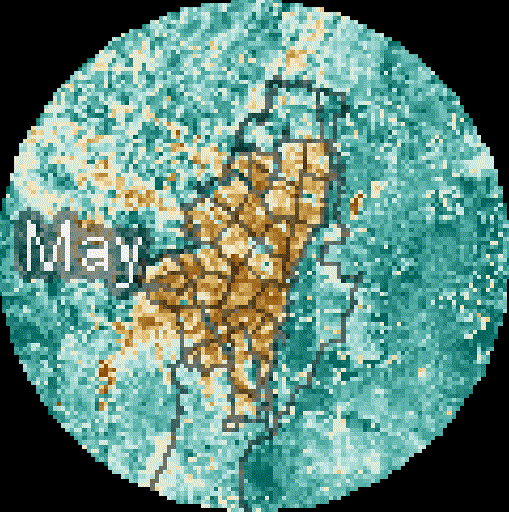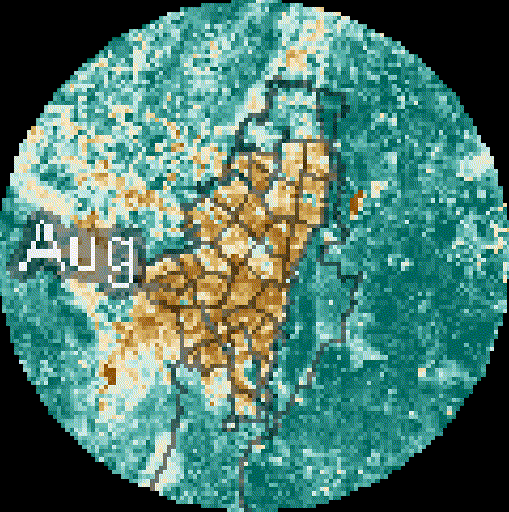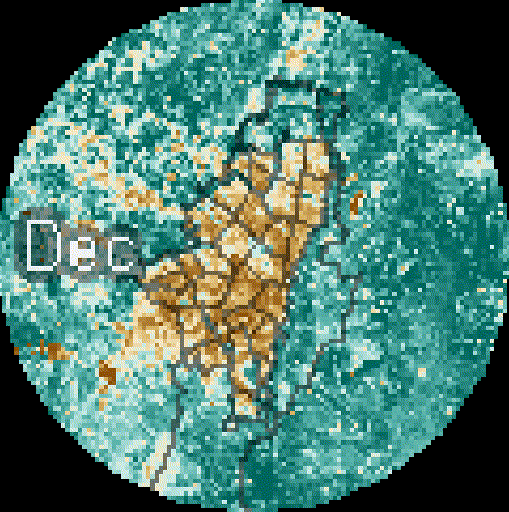
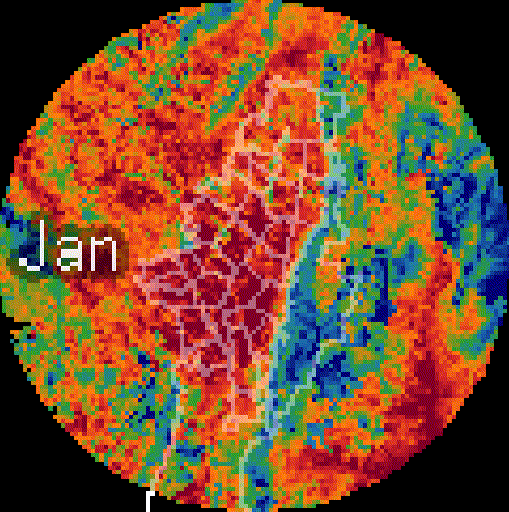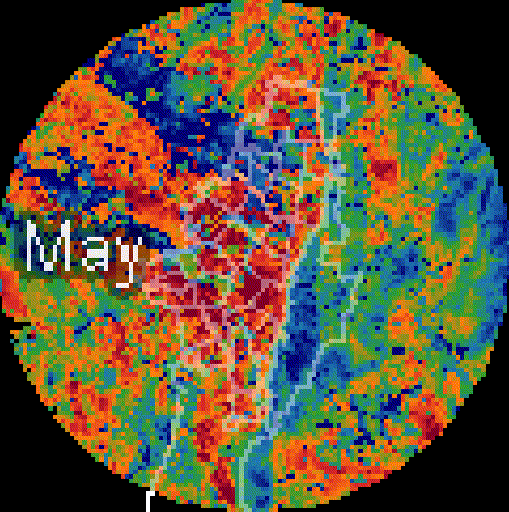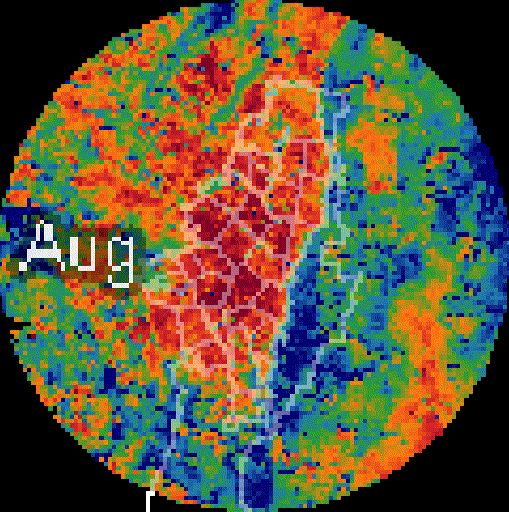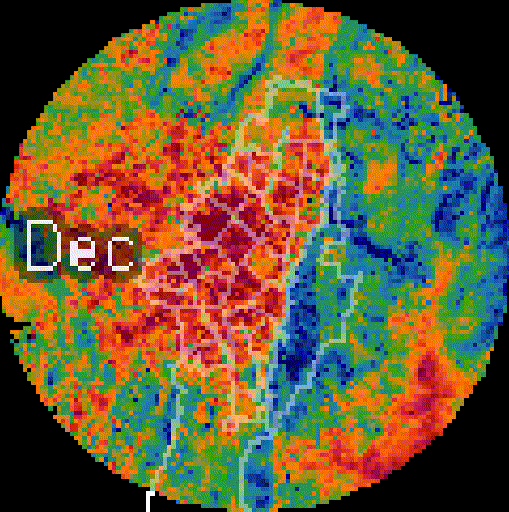
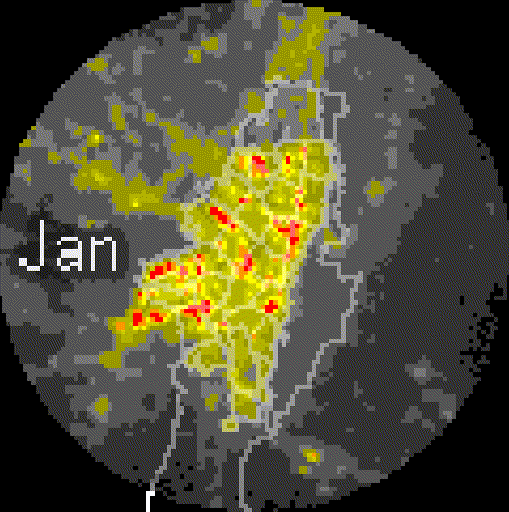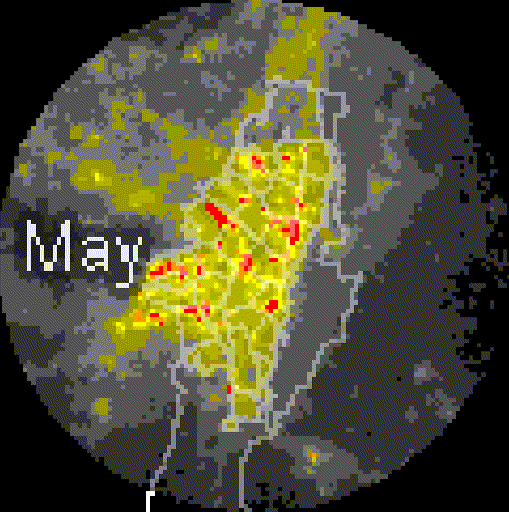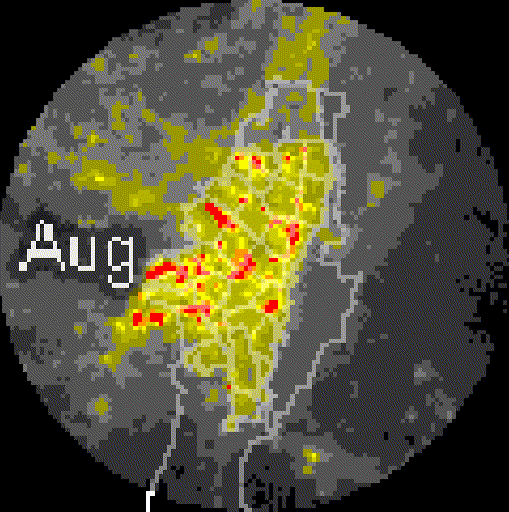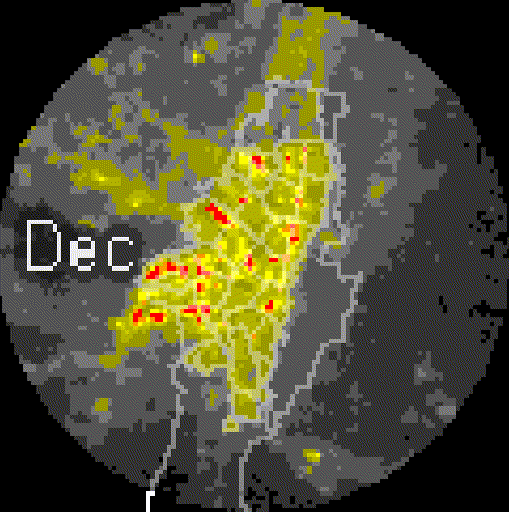
Added value
-
High spatial resolution: 100–1000 m. Enables neighborhood-scale analysis and direct support for local decision-making.
-
PM₂.₅ Downscaling to a 1km pixel resolution. Multi-dataset model (DEM, NO₂, PM coarse, population density, NTL).
-
R² = 0.861, sufficient accuracy for operational air quality monitoring.
-
Automatic identification of critical zones. Prioritization of areas with the highest simultaneous exposure to pollution, heat, low accessibility, and ecological deficit.
-
Intervention recommendations. Direct integration with urban health, climate resilience, and health sector adaptation agendas, consistent with the priorities of C40, COP30, and PAHO.
-
Fully replicable for dozens of Latin American cities, including those linked to Amazonia Forever, C40, and Healthy Municipalities networks supported by PAHO.